Is a Rotary Evaporator the Same as Distillation?
When diving into the world of chemical processing and laboratory equipment, a common question arises: Is a rotary evaporator (rotovap) the same as distillation? To unravel this, we must delve into the principles, applications, and nuances of both techniques.
Understanding Rotary Evaporators
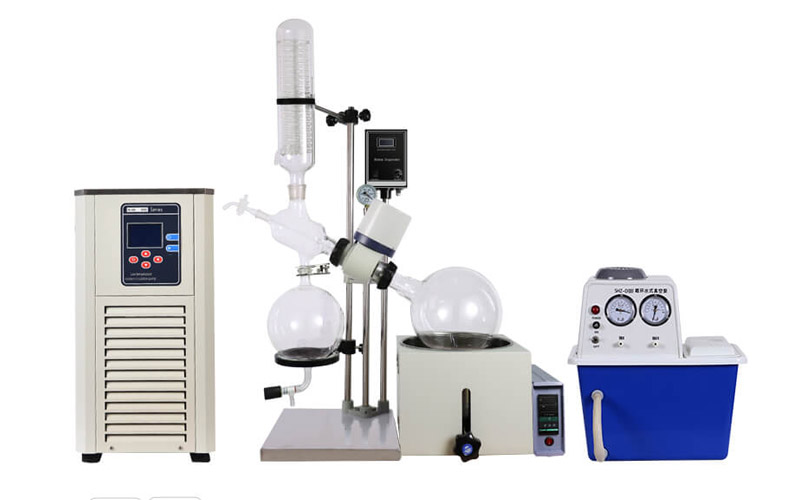
A rotary evaporator, often referred to as a rotovap, is a highly efficient apparatus used in laboratories for the purpose of evaporating solvents under reduced pressure. This technique, which involves the use of a vacuum system, rotating flask, and a heating bath, allows for the gentle and rapid removal of solvents from samples.
The principle behind a rotovap is relatively straightforward. By creating a vacuum, the boiling point of the solvent is significantly lowered, enabling evaporation at much lower temperatures. The rotating flask increases the surface area of the liquid, enhancing the efficiency of evaporation. This method is particularly valuable in chemical and biological laboratories where the preservation of temperature-sensitive compounds is critical.
Distillation: The Traditional Technique
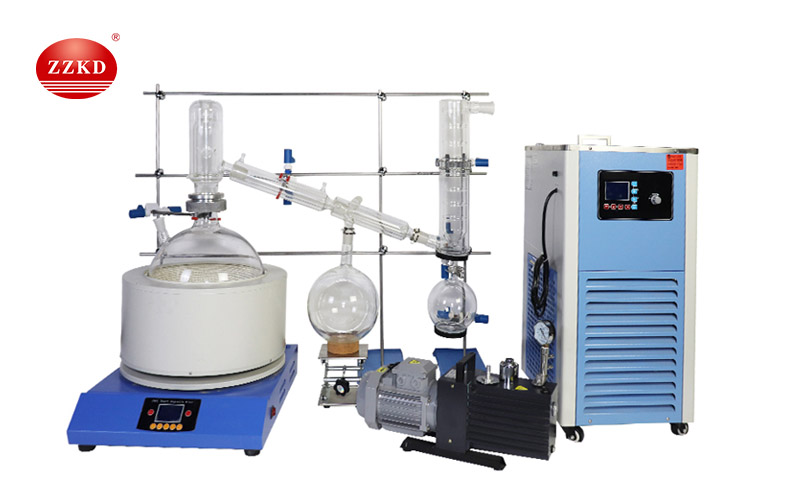
Distillation, on the other hand, is a more traditional and widely recognized method used to separate mixtures based on differences in boiling points. The process involves heating a liquid to create vapor and then cooling the vapor to collect the purified component. Distillation is a staple in industries ranging from petrochemical processing to the production of alcoholic beverages.
There are several types of distillation, including simple, fractional, and steam distillation, each suited to different types of mixtures and separation challenges. Despite its widespread use, distillation can be time-consuming and energy-intensive, particularly for mixtures with components that have similar boiling points.

Key Differences Between Rotary Evaporators and Distillation
So, is a rotovap the same as distillation?
No, they are not the same. While both techniques involve the separation of components based on volatility, the methods and applications differ significantly.
1. Process Efficiency: Rotary evaporators are designed for the efficient removal of solvents from samples, making them ideal for tasks requiring quick solvent evaporation. In contrast, distillation is better suited for the complete separation of mixtures into their individual components.
2. Temperature Control: The rotovap’s ability to operate under reduced pressure allows for evaporation at much lower temperatures, which is beneficial for heat-sensitive materials. Distillation typically requires higher temperatures to achieve separation, which can be detrimental to thermally labile compounds.
3. Application Specificity: Rotary evaporators are commonly used in laboratory settings for tasks such as solvent recovery, concentration of solutions, and sample preparation. Distillation, with its various forms, finds applications across a broader spectrum of industries, including pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and food and beverage production.

Why a rotary evaporator is preferred over traditional distillation for solvent removal in laboratories?
Rotary evaporators are preferred in laboratory settings due to their efficiency and ability to operate at lower temperatures, which is crucial for preserving the integrity of temperature-sensitive compounds. The rapid evaporation process facilitated by the rotovap also makes it a time-saving alternative to traditional distillation.
Applications of Rotary Evaporators
To further illustrate the utility of rotary evaporators, let's explore some common applications:
1. Solvent Recovery: In many chemical syntheses, the reaction medium needs to be removed after the reaction is complete. A rotovap efficiently recovers solvents, allowing for their reuse, which is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
2. Concentration of Solutions: Researchers often need to concentrate solutions to analyze minor components or to achieve a desired concentration. The rotovap excels in concentrating solutions without compromising the stability of the compounds.
3. Sample Preparation: Prior to analysis, samples often need to be prepared by removing solvents. Rotary evaporators streamline this process, ensuring samples are ready for techniques such as chromatography or spectroscopy.

Advancements in Rotary Evaporator Technology
Rotary evaporator technology has seen significant advancements over the years. Modern rotovaps come equipped with sophisticated features such as:
Digital Controls: Providing precise control over temperature and rotation speed.
Automatic Lifting: Enhancing user safety and convenience.
Improved Sealing Systems: Minimizing solvent loss and ensuring a high degree of vacuum.
These innovations have expanded the capabilities and efficiency of rotary evaporators, making them indispensable in contemporary laboratories.

Where traditional distillation is still the better choice compared to using a rotovap?
Absolutely! Traditional distillation is more suitable for the complete separation of mixtures into pure components, especially when dealing with large-scale industrial processes. While a rotovap excels at solvent recovery and concentration tasks, distillation remains the go-to method for producing high-purity products in industries like petrochemicals and alcohol production.
Distillation: Evolving with Technology
While rotary evaporators have evolved, distillation technology has not remained stagnant. Innovations in distillation techniques include:
Vacuum Distillation: Similar to rotovaps, vacuum distillation lowers the boiling points of components, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials.
Azeotropic Distillation: Addressing the challenge of separating components with similar boiling points by adding a third substance to create an azeotrope with distinct boiling characteristics.
Molecular Distillation: Used for purifying heat-sensitive compounds and high-molecular-weight substances, offering advantages in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
Choosing the Right Technique
When deciding between a rotary ethanol evaporator and traditional distillation, several factors must be considered:
1. Nature of the Mixture: For complex mixtures requiring complete separation, traditional distillation methods are preferable. For simple solvent removal and concentration tasks, a rotovap is more efficient.
2. Scale of Operation: Rotary evaporators are ideal for laboratory-scale applications, while traditional distillation can be scaled up for industrial processes.
3. Temperature Sensitivity: If the compounds being processed are heat-sensitive, a rotovap’s ability to operate at lower temperatures makes it the better choice.

While a rotary evaporator and traditional distillation share similarities in their foundational principles, they serve distinct purposes and offer unique advantages. The rotovap’s efficiency and gentle processing make it a staple in laboratories, particularly for tasks involving solvent recovery and concentration. Traditional distillation, with its versatility and comprehensive separation capabilities, remains indispensable in various industrial applications.
Have you considered how advancements in these technologies can benefit your specific applications?
By staying informed about the latest advancements in rotary evaporators and distillation technologies, you can optimize your processes, improve efficiency, and ensure the highest quality outcomes for your specific applications. Whether you’re working in a laboratory or an industrial setting, choosing the right technique and equipment is crucial for achieving your goals.
Understanding the differences and applications of rotary evaporators and distillation allows you to make informed decisions, ensuring the best outcomes for your chemical processing needs.


