How Does a Rotary Evaporator Remove Solvent?
Rotary evaporators, often referred to as rotovaps, are indispensable tools in chemistry laboratories for removing solvents from liquid samples. This process is crucial for concentrating solutions, isolating compounds, or preparing samples for further analysis. Understanding how a rotary evaporator effectively removes solvents is essential for scientists and researchers to utilize this equipment efficiently.
How Does a Rotary Evaporator Work?
At its core, a rotary evaporator operates on the principle of evaporation under reduced pressure. It consists of a heating bath, a rotating flask, a condenser, and a vacuum pump. The sample containing the solvent is placed in the rotating flask, which is then partially immersed in a heated bath. The vacuum pump creates a low-pressure environment inside the system, facilitating the evaporation of the solvent at lower temperatures than its normal boiling point.
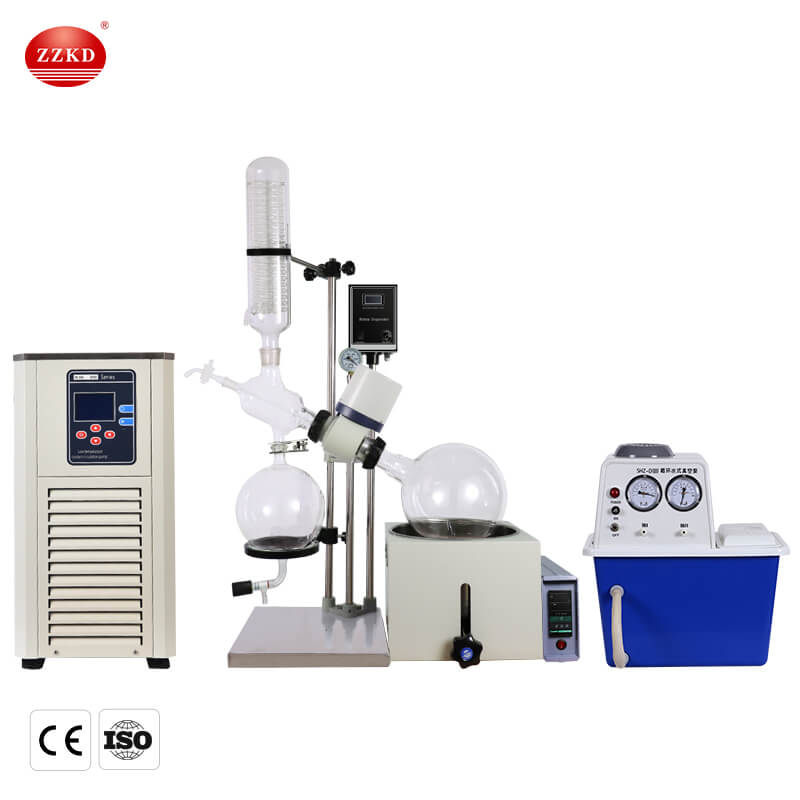

How Does a Rotary Evaporator Remove Solvent?
1. Heating the Bath: The heating bath is set to a temperature slightly below the boiling point of the solvent. This ensures that the solvent evaporates efficiently without degrading the sample or causing excessive bumping.
2. Rotating the Flask: The flask containing the sample is attached to a motor-driven shaft, causing it to rotate slowly. This rotation increases the surface area of the liquid exposed to the heated bath, enhancing the evaporation process.
3. Lowering the Pressure: The vacuum pump connected to the system removes air and other gases, creating a reduced pressure environment within the apparatus. This lowers the boiling point of the solvent, allowing it to evaporate at a lower temperature.
4. Condensation: As the solvent evaporates from the sample, it rises and enters the condenser, which is typically cooled with a circulating coolant such as water. The condenser converts the vapor back into a liquid form, which is then collected in a separate container.
5. Collection of Residue: Once the solvent is removed, the desired residue, such as a concentrated solution or purified compound, remains in the flask for further processing or analysis.
Advantages of Rotary Evaporation:
Gentle Evaporation: The low temperature and reduced pressure environment minimize the risk of sample degradation or loss of volatile compounds.
Efficiency: The combination of heat, rotation, and vacuum accelerates the evaporation process, allowing for faster solvent removal compared to traditional methods.
Versatility: Rotary evaporators are adaptable to a wide range of solvents and sample types, making them versatile tools in various scientific applications.
Rotary Evaporator Related Equipment:
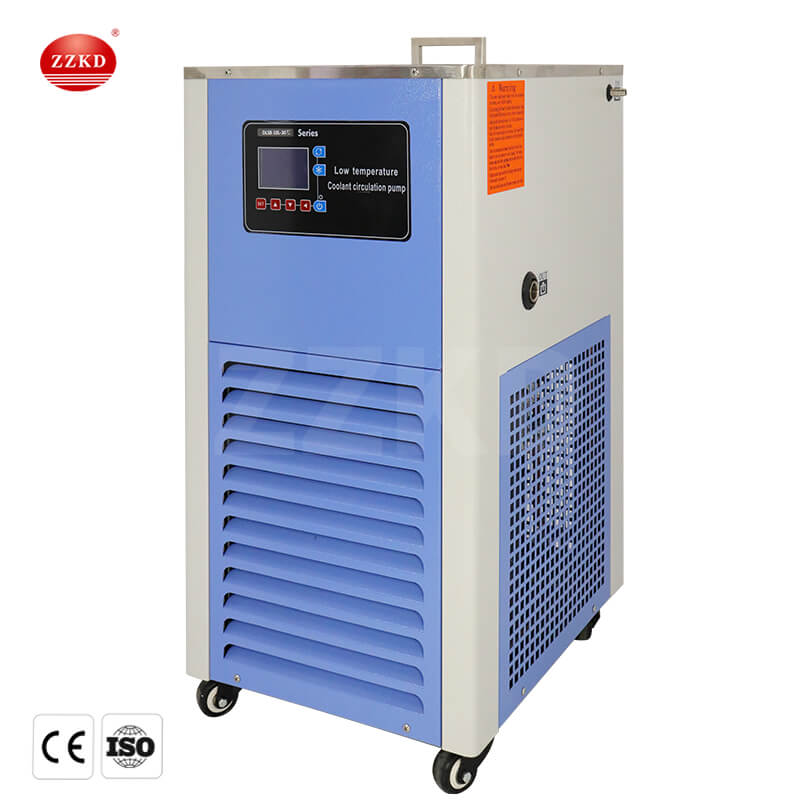
When operating a rotary evaporator, it is usually necessary to equip it with some accessory equipment to provide necessary conditions and support. Two of the main supporting equipment are cryogenic cooling circulation pumps and circulating water vacuum pumps.
1. Low Temperature Coolant Circulation Pump: During operation, a rotary evaporator generates heat and requires cooling to maintain a stable operating temperature for effective experimentation. The low temperature coolant circulation pump is a device designed to provide continuous cooling by circulating a cooling fluid. Typically, this pump draws cooling fluid (usually water or a specific coolant) from a low-temperature reservoir, passes it through the equipment for cooling, and then returns it to the reservoir in a continuous cycle. This helps control the internal temperature of the rotary evaporator, preventing the sample from overheating.

2. Water Circulating Vacuum Pump: A rotary evaporator operates under vacuum conditions to lower the boiling point of the sample, facilitating more efficient evaporation. The water circulating vacuum pump is a device used to create the necessary vacuum environment. It operates by evacuating air from the container, thus reducing the pressure and creating a vacuum. This type of pump typically uses water as the working medium, expelling water from the pump to create a vacuum and then discharging the expelled water and air from the system. The water circulating vacuum pump ensures that the rotary evaporator operates under the required vacuum conditions, facilitating efficient evaporation and separation of the sample.
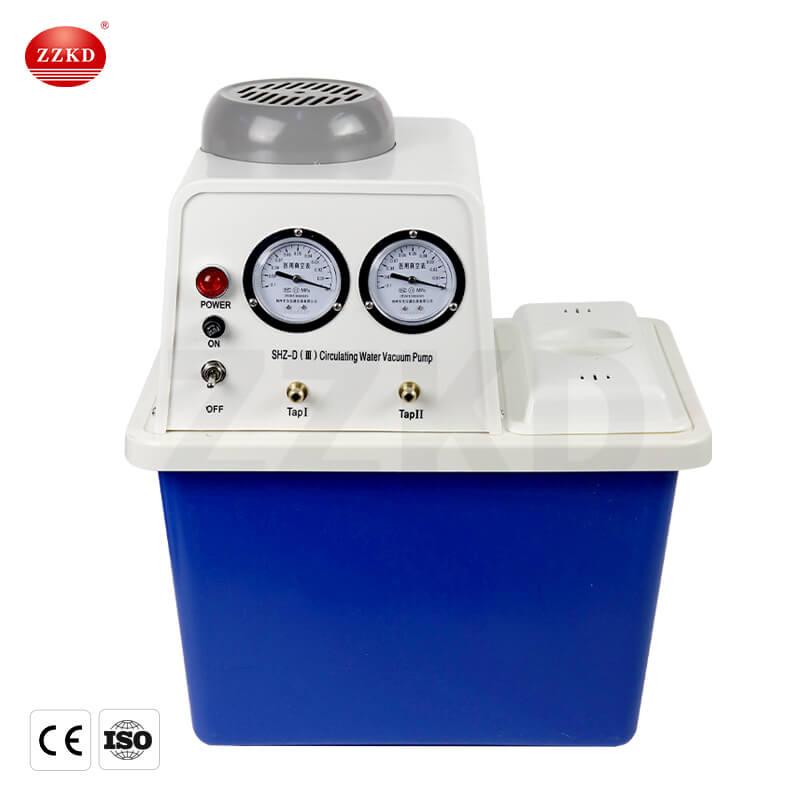

These two complementary devices provide the necessary operational conditions for a rotary evaporator, enabling it to efficiently perform the task of separating mixtures. The low temperature coolant circulation pump maintains a stable operating temperature, while the water circulating vacuum pump creates the required vacuum environment, ensuring the proper functioning of the rotary evaporator.
Is It Beneficial for Businesses to Invest in a Rotary Evaporator for Solvent Removal?
Indeed, investing in a rotary evaporator for solvent removal can offer significant advantages for businesses. However, the magnitude of these benefits varies depending on the specific needs and goals of the company. When considering such an investment, businesses often have diverse motivations. Some prioritize reducing costs associated with solvent usage in their processes, while others focus on improving efficiency and productivity. Similar to customers considering various factors when selecting products, such as price, quality, and reliability, businesses must also carefully assess different aspects to choose the most suitable rotary evaporator for their operations.
How Can Businesses Determine the Right Rotary Evaporator for Solvent Removal?
Businesses can assess their requirements based on factors such as the volume of solvent to be removed (daily or monthly) and the types of processes involved. Rotary evaporators come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different production capacities and solvent types. By estimating their solvent removal volume and considering factors such as evaporation efficiency, scalability, and ease of operation, businesses can select the appropriate rotary evaporator model. For instance, smaller-scale operations may benefit from a benchtop rotary evaporator, while larger facilities may require a larger-scale industrial unit. These decisions should align with the company's production objectives and operational requirements.

What Are the Key Advantages of Investing in a Rotary Evaporator for Solvent Removal?
Investing in a rotary evaporator for solvent removal offers several key advantages for businesses. Firstly, it enables efficient and precise removal of solvents from solutions, minimizing solvent wastage and reducing overall costs. Additionally, rotary evaporators are versatile and can be used for various solvent removal applications, including concentration, drying, and purification. Moreover, these units are designed for ease of operation and maintenance, ensuring smooth integration into existing production workflows. Ultimately, investing in a rotary evaporator for solvent removal allows businesses to optimize their solvent usage, improve process efficiency, and maintain competitiveness in the market.


